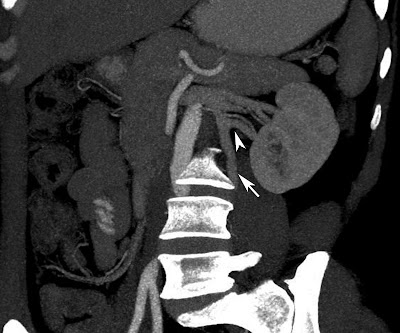
Axial CT of kidneys in a 29 year old male showing small exophytic fat attenuation lesion in the left kidney (arrow) suggestive of angiomyolipoma.
Zoomed picture of the above showed image better shows the lesion.
Discussion:
Angiomyolipoma (AML) is the most common benign tumour of the kidney and is composed of blood vessels, smooth muscle cells and fat cells. It is strongly associated with tuberous sclerosis.
Imaging features:
Ultrasonography (USG) - Well defined hyper echoic lesion in the kidney. Hyperechogenecity is due to fat content of the lesion.
CT Scan: Well defined fat attenuation lesion as shown in our case. CT angiography may be helpful to identify the aneurysms which predict the fatal hemorrhage.
MRI - Hyperintense on both T1 and T2 weighted images due to its fat content and appears hypointense on fat suppressed T1 images.
If the fatty tissue is scanty in-phase and out-phase images T1 weighted sequence is very helpful in identifying the fat component in the lesion, which is seen as loss of signal on out-phase images.
People with tuberous sclerosis needs yearly follow up renal scans.
Treatment:
- If the lesion is < 4 cm - follow up imaging to look for the progression of the lesion.
- If it is > 4 cm or presence of aneurysm, needs to be treated with trans arterial embolisation or surgical excision. Embolising agents used are PVA (Polyvinyl alcohol) and absolute alcohol mixed with lipiodol.